[spring] Spring Security
참고하면 좋은 사이트 :
https://www.bezkoder.com/spring-boot-jwt-auth-mongodb/
참고 교재 : 스프링 인 액션
지은이 : 크레이그 월즈 , 옮긴이 : 심재철
Spring Security
- Spring Security 를 사용하면, Spring Security 가 제공하는 Login Form 을 사용해야된다.
- 이 Login Form 은 다른 Form 으로 변경해서 사용할 수 있다.
Spring Security 라이브러리 다운받기
- pom.xml 에 spring-security 의존 명시해서 다운받기
pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Intelli J 프리미엄 에디션을 사용중이라면 다음과 같이 간단하게 추가시킬수 있다.
- 프로젝트 오른쪽 클릭
- add framework support…
- 밑으로 쭉 내려서 spring security 선택후 적용
Spring Security 환경설정하기
- 따로 설정만 관리하는 config 폴더를 생성한다. 거기서 환경설정을 관리하게 한다.
- config 폴더에 Spring Security 환경설정 기능을 수행하는 커스텀 클래스를 작성한다.
- 클래스 이름은 SecurityConfigureation 혹은 SecurityConfig 등등으로 짓는다.
(중요) WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 를 클래스에 상속시켜서 사용한다.
- extend WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 에서 사용하는 오버라이딩 메소드 정리
- configure(HttpSecurity) : HTTP 보안을 구성하는 메소드
- configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder) : 사용자 인증 정보를 구성하는 메소드
- 사용자 스토어(store : 저장)를 구성할때 이 메서드에서 구성한다.
- 위의 configure() 두개의 메소드를 사용하여 URL 에 대한 보안설정, 사용자 인증 저장방법 두개를 구성해야된다.
사용자 스토어
- 한 명 이상의 사용자를 처리할 수 있도록 사용자 정보를 유지*관리하는 사용자 스토어를 구성해야 된다.
- 스프링 시큐리티에서는 다음과 같은 사용자 스토어 구성방법을 제공한다.
- 인메모리(in-memory 사용자 스토어)
- JDBC 기반 사용자 스토어
- LDAP 기반 사용자 스토어
- 커스텀 사용자 명세 서비스
- Spring Security Config (AuthenticationManagerBuilder) 를 오버라이딩 해서 스토어를 구성한다.
인메모리 사용자 스토어
- 사용자 정보를 메모리에 저장해 유지 / 관리
- 테스트 목적이나 간단한 애플리케이션에 편리하다.
- 하지만 사용자 정보의 추가 / 삭제 / 변경이 어렵다는 단점이 있다.
- 보안 구성 코드를 변경한 후 애플리케이션을 다시 빌드하고 배포, 설치해야 한다.
인메모리 스토어 사용 예제
- user1 과 user2 를 인메모리 사용자 스토어에 구성한다.
@Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { super.configure(auth); auth.inMemoryAuthentication() .withUser("user1") // 이 메소드를 호출하면 사용자의 구성이 시작된다. // 사용자 이름을 인자로 전달한다. .password("{noop}password1") // 비밀번호를 인자로 전달한다. // {noop} 을 지정하면 비밀번호를 암호화하지 않는다. // spring 5 부터는 반드시 비밀번호를 암호화 해야 하므로 만약 암호화 되어있지않으면 403 또는 500 에러가 발생한다. .authorities("ROLE_USER") // 권한의 명칭(이름) 은 마음대로 지정할수 있다. .and() .withUser("user2") .password("{noop}password2") .authorities("ROLE_USER"); }
JDBC 기반의 사용자 스토어
- 데이터 베이스 (DB) 를 기반으로 사용자의 정보를 유지 / 관리를 한다.
- 로그인을 하면, DB에 값이 insert 되고, 권환조회를 하면 DB에서 값을 가져와 권한을 조회한다.
- 비밀번호를 암호화 하지 않으면 500 에러가 발생한다.
- spring 5 부터는 의무적으로 PasswordEncoder를 사용해서 비밀번호를 암호화 해야하기 때문이다.
- javax.sql.DataSource 를 사용해서 sql 파일을 작성해야 한다.
- sql 파일을 src/main/resources 아래에 작성하면, 애플리케이션이 시작될 때 sql파일의 sql이 데이터 소스로 지정된 데이터베이스에서 자동 실행된다.
- usersByUsernameQuery( 쿼리 string ) 과 authoritiesByUsernameQuery ( 쿼리 string ) 을 사용하면 .sql 파일보다 먼저 실행된다. (대체할 수 있다.)
- 다음과 같은 사항을 지켜야한다.
- 매개변수는 하나이며, username 이어야 한다.
- 사용자 정보 인증 쿼리에서는 username, password, enabled 열의 값을 반환해야 한다.
- 사용자 권한 쿼리에서는 해당 사용자 이름 username 과 부여된 권한 authority을 포함하는 0 또는 다수의 행을 반환할 수 있다.
- 그룹 권한 쿼리에서는 각각 그룹 id, 그룹 이름 group_name, 권한 authority 열을 갖는 0 또는 다수의 행을 반환할 수 있다.
JDBC 기반의 사용자 스토어 사용 예제
...
import javax.sql.DataSource;
...
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
// @Autowired 사용으로 의존이 자동으로 스프링에 주입된다.
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
super.configure(auth);
auth.jdbcAuthentication()
.dataSource(dataSource)
.usersByUsernameQuery(
"select username, password, enabled from users" +
"where username=?")
.authoritiesByUsernameQuery(
"select username, authority from authorities " +
"where username=?");
.passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder());
// 비밀번호를 암호화 해서 사용한다. 상세내용은 다음 문단에 설명
}
암호화된 비밀번호 사용하기
- DB에 사용자 정보가 저장될때 비밀번호가 평문으로 저장되면 해커의 먹이가 된다.
- 비밀번호를 암화해서 데이터베이스에 저장하면, 사용자가 입력한 평범한 텍스트의 비밀번호화 일치하지 않기 때문에 인증에 실패할 것이다.
- 따라서 비밀번호를 데이터베이스에 저장할 때와 사용자가 입력한 비밀번호는 모두 같은 암호화 알고리즘을 사용해서 암호화 해야한다.
비밀번호를 암호화 할때는 passwordEncoder() 메소드를 호출하여 비밀번호 인코더를 지정한다.
passwordEncoder()
- 스프링 시큐리티의 PasswordEncoder 인터페이스를 구현하는 어떤 객체도 인자로 받을 수 있다.
- 인자로 들어가는 PasswordEncoder 인터페이스 구현체 종류
- BCryptPasswordEncoder : bcrypt를 사용. 해싱 암호화 한다.
- NoOpPasswordEncoder : 암호화 하지 않는다.
- Pbkdf2PasswordEncoder : PBKDF2를 사용. 암호화 한다.
- ScrptPasswordEncoder : scrypt를 해싱 사용. 암호화 한다.
- StandardPasswordEncoder : SHA-256 을 사용. 해싱 암호화 한다.
- 어떤 비밀번호 인코더를 사용하든, 일단 암호화되어 데이터베이스에 저장된 비밀번호는 암호가 해독되지 않는다.
- 대신 로그인 시에 사용자가 입력한 비밀번호와 동일한 알고리즘을 사용해서 암호화된다.
- 그 다음, 데이터베이스의 암호화된 비밀번호 와, 사용자가 로그인해서 암호화된 비밀번호화 비교를 수행한다.
- 이 일은 PasswordEncoder 의 matches() 메서드에서 수행된다.
- 커스텀 클래스를 만들어서 예를들면 Test.java 그리고 implements PasswordEncoder 를 한뒤에
- encode() 메소드와 matches() 메소드를 오버라이딩해 구현한다음에
- new test() 를 passwordEncoder()의 인자로 집어넣을 수 있다.
- 예) passwordEncoder(new Test())
LDAP 기반의 사용자 스토어
- 생략
커스터마이징 사용자 스토어
(1) user 모델에 다음과 같은 클래스를 implements 한다.
- implements UserDetails
- 필요한 메소드들을 오버라이딩 추가한다.
- getAuthorities() : 갖고있는 권한들을 리스트로 묶어서 가져오는 메소드
- isAccountNonLocked(), isAccountNonExpired(), isCredentialsNonExpired(), isEnabled() : 해당 사용자 계정의 활성화 또는 비활성화 여부
- getUsername()
- user의 id 를 갖고올수 있도록 리턴값을 바꾼다.
- getPassword()
- user의 password 를 갖고올수 있도록 리턴값을 바꾼다.
(2) 해당 유저의 권한을 갖고오는 service, mapper , xml mapper 등을 만든다.
(3) 따로 User 정보를 갖고올 Service 클래스를 생성해 UserDetailService 를 implements 해서 구현한다.
- loadUserByUsername() 를 오버라이딩 해서 구현해줘야 한다.
- 절대로 null 을 반환하면 안된다.
- null 을 반환하면 발생하는 Not found Exception을 구현해줘야 한다.
예제 코드
@Service
public class StudyUserService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
StudyUserMapper studyUserMapper;
...
...
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String user_id) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
StudyUser studyUser = studyUserMapper.selectByID(user_id);
// DB에서 user_id 를 인자로 테이블에 존재하면 가져온다.
if(studyUser != null){
return studyUser;
}
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("User '"+ user_id +"' not found in Database");
}
}
(4) 다시 Spring Security config 로 돌아와서 auth.userDetailesSErvice( ) 에 UserDetailService 를 집어넣는다.
예제 코드)
....
....
....
@Autowired
private StudyUserService userDetailService;
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
super.configure(auth);
auth
.userDetailsService(userDetailService);
}
(5) 데이터베이스에서 가져온 사용자 비밀번호가 암호화 되도록 비밀번호 인코더를 구성해야 한다.
- PasswordEncoder 타입의 빈을 선언한다.
- passwordEncoder() 를 호출하여 이 빈을 사용자 명세 서비스 구성에 주입하게 하면 된다.
예제 코드)
...
...
...
@Autowired
private StudyUserService userDetailService;
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
super.configure(auth);
auth
.userDetailsService(userDetailService)
.passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
// password 암호화
// passwordEncoder에 bean 어노테이션이 등록되었으므로 BCryptoPasswordEncoder 인스턴스가 스프링 애플리케이션 컨텍스트에 등록, 관리된다.
// 이 인스턴스가 애플리케이션 컨텍스트로부터 주입되어 반환된다.
// 이렇게 함으로써 우리가 원하는 종류의 PasswordEncoder 빈 객체를 스프링의 관리하에 사용할 수 있다.
}
(6) 회원가입시 DB에 저장되는 사용자 password 를 암호화 해서 DB에 저장하도록 구현한다.
- Spring Security configure 에서 설정한 동일한 알고리즘을 사용해서 암호화 해야된다.
- 동일한 알고리즘을 사용해야 DB의 암호, 사용자가 로그인한 암호를 비교할수 있다.
컨트롤러 단 예제
...
...
...
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@PostMapping("/insertUser")
public int insertUser(@RequestBody StudyUser studyUser){
String encrypted_password = (passwordEncoder.encode(studyUser.getPassword()));
studyUser.setPw(encrypted_password);
// 가입 요청받은 계정의 패스워드를 암호화 해서 재설정
return studyUserService.insertUser(studyUser);
}
// 유저 정보 생성
Spring Security Configure(HttpSecurity http) 환경설정하기
- WebSecurityConfigurerAdpater 를 extend 해야된다.
- configure(HttpSecurity http) 를 오버라이딩 한다.
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
...
}
HttpSecurity 인자를 사용해서 구성 할수 있는 것들
- HTTP 요청 처리를 허용하기 전에 충족되어야 할 특정 보안 조건을 구성한다.
- 커스텀 로그인 페이지를 구성한다.
- 사용자가 어플리케이션의 로그아웃을 할 수 있도록 한다.
- CSRF 공격으로부터 보호하도록 구성한다.
HttpSecurity 에서 사용하는 메소드들
- 해당 구성 연결이 끝나고 다음 구성을 설정할때는 and() 메소드를 사용한다.
-
and() 메서드는 인증 구성이 끝나서 추가적인 HTTP 구성을 적용할 준비가 되었다는 것을 나타낸다.
authorizeRequests()
- ExpressionInterCeptUrlRegistry 객체를 반환한다.
- antMatchers(“url”) 을 사용하여 해당 url 에 대한 처리를 정한다.
- access(String) : 인자로 전달된 SpEL 표현식이 true면 접근을 허용한다.
- anonymous() : 익명의 사용자에게 접근을 허용한다.
- authenticated() : 익명이 아닌 사용자로 인증된 경우 접근을 허용한다.
- denyAll() : 무조건 접근을 거부한다.
- fullyAuthenticated() : 익명이 아니거나 또는 remember-me 가 아닌 사용자로 인증되면 접근을 허용한다.
- hasAnyAuthority(String…) : 지정된 권한 중 어떤 것이라도 사용자가 갖고 있으면 접근을 허용한다.
- hasAnyRole(String…) : 지정된 역할 중 어느 하나라도 사용자가 갖고 있으면 접근을 허용한다.
- hasAuthority(String) : 지정된 권한을 사용자가 갖고 있으면 접근을 허용한다.
- hasIpAddress(String) : 지정된 IP 주소로부터 요청이 오면 접근을 허용한다.
- hasRole(String) : 지정된 역할을 사용자가 갖고 있으면 접근을 허용한다.
- not() : 다른 접근 메서드들의 효력을 무효화 한다.
- permitAll() : 무조건 접근을 허용한다.
- rememberMe() : remember-me(이전 로그인 정보를 쿠키나 데이터베이스로 저장한 후 일정 기간 내에 다시 접근시 저장된 정보로 자동 로그인됨)를 통해 인증된 사용자의 접근을 허용한다.
- 위의 각 메서드에서 정의된 보안 규칙만 사용된다는 제약이 있다.
- SpEL(Spring Expression Language)
- 스프링 시큐리티에서는 SpEL을 확장하여 보안 관련 특정 값과 함수를 갖고 있다.
- access(SpEL 표현식 문자열) 메소드를 사용해서 적용한다. 표현식이 true면 접근을 허용 한다.
- authentication : 해당 사용자의 인증 객체
- denyAll : 항상 false를 산출한다.
- hasAnyRole(역할 리스트) : 지정된 역할 중 어느 하나라도 해당 사용자가 갖고 있으면 true
- hasRole(역할) : 지정된 역할을 해당 사용자가 갖고 있으면 true
- hasIpAddress(IP 주소) : 지정된 IP 주소로부터 해당 요청이 온 것이면 true
- isAnonymous() : 해당 사용자가 익명 사용자면 true
- isAuthenticatied() : 해당 사용자가 익명이 아닌 사용자로 인증 되었으면 true
- isFullyAuthenticated() : 해당 사용자가 익명이 아니거나 또는 remember-me 가 아닌 사용자로 인증되었으면 true
- isRememberMe() : 해당 사용자가 remember-me 기능으로 인증되었으면 true
- permitAll : 항상 true를 산출한다.
- principal : 해당 사용자의 principal 객체
SpEL 사용예제
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/design","orders").access("hasRole('ROLE_USER')")
.antMatchers("/","/**").access("permitAll")
.anyRequest().authenticated();
}
formLogin()
- 스프링 시큐리티의 기본제공 LoginForm 을 설정 변경한다.
formLogin() 메소드들
- loginPage() : 로그인 페이지로 지정할 url. 인증되지 않으면 해당 url 로 자동 리다이렉트 된다.
- loginProcessingUrl() : 유저name 과 password 를 제출할 url
- defaultSuccessUrl() : 로그인이 성공하고 난 다음에 이동할 url
- 두번째 인자로 true 를 전달하면 사용자가 로그인 전에 어떤 페이지에 있었는지와 무관하게 로그인 후에는 무조건 해당 url 로 이동되어진다.
- failureUrl() : 로그인이 실패할시에 이동할 url
- usernameParameter(“유저네임 혹은 ID “) : 해당 변수로 user의 id를 받아온다.
- passwordParameter(“패스워드로 사용할 변수”) : 해당 변수로 user의 password 를 받아온다.
logout()
- 로그아웃을 하기 위해서 설정하는 메소드
logoutSuccessUrl(“url”) : 로그아웃이 성공한 후의 이동할 url. 설정을 안하면 자동으로 Login 페이지로 이동되어진다.
CSRF 공격의 의미
CSRF(Cross-Site Request Forgery) 크로스 사이트 요청 위조
- 사용자가 웹사이트에 로그인한 상태에서 악의적인 코드(사이트 간의 요청을 위조하여 곡격하는)가 삽입된 페이지를 열면 공격 대상이 되는 웹사이트에 자동으로 폼이 제출된다.
- 이 사이트는 위조된 공격 명령이 믿을 수 있는 사용자로부터 제출된 것으로 판단하게 되어 공격에 노출된다.
- CSRF 공격을 막기 위해 어플리케이션에서는 폼의 숨김(hidden) 필드에 넣을 CSRF 토큰(token)을 생성할 수 있다.
- 해당 필드에 토큰을 넣은 후 나중에 서버에서 사용한다.
- 이후에 해당 폼이 제출될 때는 폼의 다른 데이터와 함께 토큰도 서버로 전송된다.
- 서버에서는 이 토큰을 원래 생성되었던 토큰과 비교하며, 토큰이 일치하면 해당 요청의 처리를 한다.
- 토큰이 일치하지 않는다면 해당 폼은 토큰이 있다는 사실을 모르는 악의적인 웹사이트에서 제출된 것이다.
스프링 시큐리티에서의 CSRF 방어
- 스프링 시큐리티에서는 CSRF 방어기능을 설정할 수 있다.
- CSRF 기능은 자동으로 활성화 되어있어서 별도로 설정할 필요가 없다.
- CSRF 토큰을 넣을 _csrf 이름의 필드를 애플리케이션이 제출하는 폼에 포함시키면 된다.
- REST API 에서 서버로 실행되는 어플리케이션의 경우 다음과 같이 CSRF 방어를 비활성화 해줘야 한다.
.csrf().disable();
로그인 중인 사용자의 정보 관리하기
@ManyToOne 어노테이션
- javax.persistence.ManyToOne
- 모델 개체에서 이 어노테이션을 달고 다른 개체를 선언하면, 현재 개채는 선언한 개체에 속하게 된다.
@Data
public class Order implements Serializable{
...
private Date placedAt;
@ManyToOne
private User user;
...
}
로그인한 사용자의 정보를 다른 모델 객체에 주입하는 방법
- Principal 객체를 컨트롤러 메서드에 주입한다.
- Authentication 객체를 컨트롤러 메서드에 주입한다.
- SecurityContextHolder를 사용해서 보안 컨텍스트를 얻는다.
- @authenticationPrincipal 어노테이션을 사용해서 컨트롤러에 주입한다.
Principal을 이용해 로그인 사용자의 정보를 가져오는 방법
- 보안과 관련없는 코드가 혼재한다는 단점이 있다.
@PostMapping
public String processOrder(@valid Order order, Errors errors, SessionStatus sessionStatus, Principal principal) {
...
User user = userRepository.findByUsername(principal.getName());
// priciipal.getName() 을 이용해 로그인한 사용자의 이름을 가져온다.
order.setUser(user);
...
}
Authentication 객체로 로그인 사용자의 정보를 가져오는 방법
@PostMapping
public String processOrder(@valid Order order, Errors errors, SessionStatus sessionStatus, Authentication authentication) {
...
User user = (User) authentication.getPrincipal();
// authentication.getPrincipal() 을 이용해 로그인한 사용자의 정보를 가져온다.
// getPrincipal() 은 java.util.Object 타입을 반환하므로 USer 타입으로 변환해야 한다.
order.setUser(user);
...
}
@AuthenticationPrincipal 을 이용해 사용자 모델을 인자로 전달해서 정보를 얻는방법
- 이 방법은 사용자 모델에 @AuthenticationPrincipal 어노테이션을 지정해야 한다.
- 이 방법의 장점은 타입 변환이 필요없다
- Authentication 과 동일하게 보안 특정 코드만 갖는다.
import org.springframework.security.core.annotation.AuthenticationPrincipal;
...
import tacos.User;
@PostMapping
public String processOrder(@valid Order order, Errors errors, SessionStatus sessionStatus, @AuthenticationPrincipal User user) {
...
if (errors.hasErrors()){
return "orderForm";
}
order.setUser(user);
sessionStatus.setComplete();
...
}
SecurityContextHolder를 사용해서 보안 컨텍스트를 얻어서 로그인 사용자의 정보를 얻는방법
- 보안 컨텍스트로부터 Authentication 객체를 얻은 후 principal 객체를 요청한다.
- 반환되는 객체를 User 타입으로 변환해야 한다.
- 컨트롤러의 처리 메서드는 물론이고, 애플리케이션의 어디서든 사용할 수 있다.
@PostMapping
public String processOrder(@valid Order order, Errors errors, SessionStatus sessionStatus) {
...
Authentication authentication =
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
// 보안 컨텍스트로부터 Authentication 객체를 얻는다.
User user = (User) authentication.getPrincipal();
// Principal 객체를 요청해 로그인 사용자의 정보를 얻는다.
...
}
Spring Security Config 환경설정하는 전체 소스코드
- 해당 permit() 한 url 을 제외한 모든 요청에 대해서 401을 리턴한다.
SecurityConfiguration.java
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private AuthProvider authProvider;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/api/back/board/welcome").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/api/back/user/login").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginProcessingUrl("/api/back/user/login")
.usernameParameter("id")
.passwordParameter("password")
.and()
.exceptionHandling()
.authenticationEntryPoint(new HttpStatusEntryPoint(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED));
}
}
스프링 시큐리티 환경설정에서 할수 있는 것들
- 사용자의 HTTP 요청 경로에 대해 접근 제한과 같은 보안 관련 처리를 우리가 원하는 대로 할 수 있게 해준다.
- 어떤 요청에 대해서 인증을 요구할 것인지
- 특정 요청에 대해서 어떤 권한을 요구할 것인지
- 인증되지 않은 요청을 어떤 url로 redirect시킬지
- 로그인 성공 후 어느 화면으로 이동시킬지
- 로그아웃시 어떤 작업을 수행시킬지
- 403에러에 대해 어떻게 처리할지
- Authentication 유효성을 어떻게 판단할지
Spring Security 사용 로그인 처리하기
참고사이트 :
https://soon-devblog.tistory.com/5?category=1026232
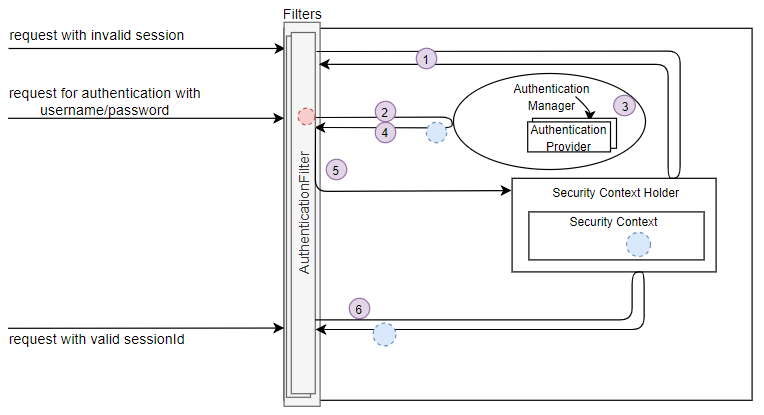
- Spring-scurity를 사용하면 모든 요청은 Session을 발급받는다.
-
Session을 발급받으면 클라이언트의 쿠키에 JESSIONID라는 키로 SessionID가 저장된다.
-
AuthenticationFilter는 해당 요청의 JESSIONID(SessionID)를 확인하여 JESSIONID와 매핑되는 인증정보가 Security Context에 있는지 판단한다.
-
JESSIONID(SessionID)에 매핑되는 인증정보가 Security Context 내에 없으면 HTTP Error Code 를 발생시키거나, 리다이렉트 처리를 할 수 있다.
-
- AuthenticationFilter 는 기본적으로 로그인폼으로 오는 데이터를 username과 password로 인식하고 있다.
- Spring Security는 자동으로 HTML Login Form을 생성한다.
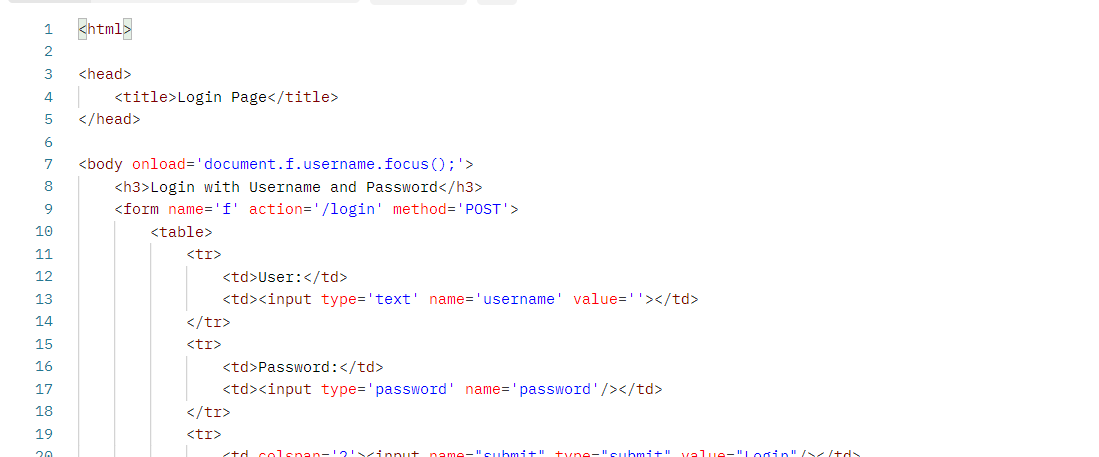
- 따라서 처리하려는 로그인 데이터 양식도 생성된 Login Form 에 맞춰서 username / password 로 변수명을 통일시켜줘야 한다.
- Spring-security는 dafault 설정으로 Mapping URL을 /login 으로 설정했는데, 프론트에서 오는 로그인 요청도 /login 으로 통일시켜 줘야한다.
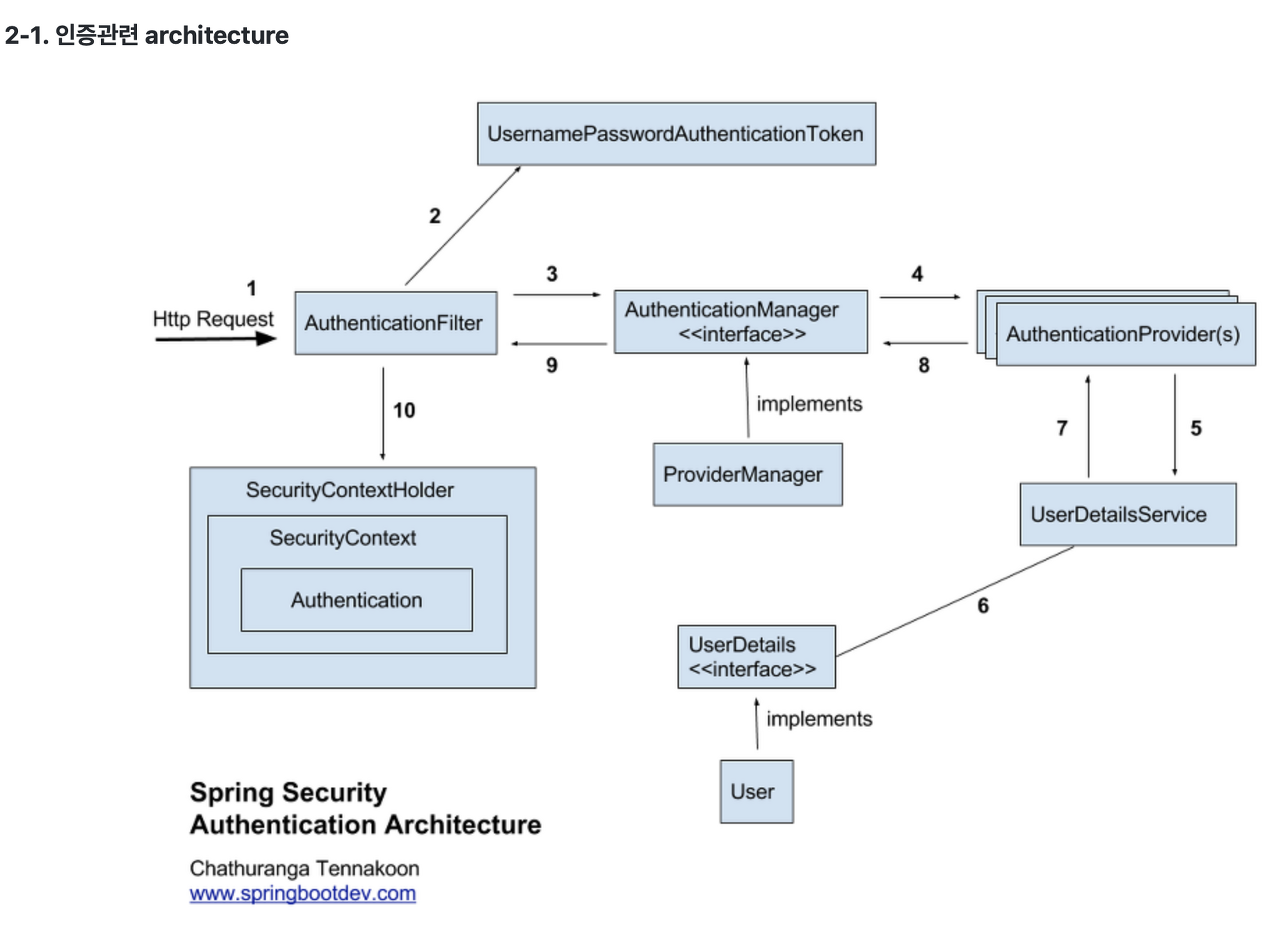
- AuthenticationFilter는 입력받은 username / password를 이용해 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 을 만든다.
- 통칭 AuthenticationToken 은 Authentication 인터페이스의 구현체다.
- AuthenticationToken에 있는 username / password가 유효한 계정인지 판단하기 위해 AuthenticationMangaer에게 위임한다.
- AuthenticationManager는 등록한 AuthenticationProvider들을 연쇄적으로 실행시킨다.
- AuthenticationProvider의 구현체에서는 다음과 같은 작업이 필요하다.
- (1). AuthenticationToken에 있는 계정 정보가 유효한지 판단하는 로직 (DB로부터 조회)
- (2). 계정 정보가 유효하다면 유저의 상세정보(이름, 나이 등 필요한 정보)를 이용해 새로운 UserPasswordAuthenticationToekn 을 발급
- 새롭게 발급받은 AuthenticationToken은 Security Context에 저장된다.
- 계정 정보가 유효하다면 AuthenticationFilter는 AuthencationSuccessHandler에 따라 요청을 redirect 시킨다.
요약
Session을 발급받는다 ->
클라이언트 쿠키에 JSSESSIONID 가 생성된다. ->
filter는 JSSESSIONID 가 Security context에 있는지 확인한다 ->
있으면 Token을 발급시킨다 ->
Manager는 등록한 Provider들을 연쇄 실행시킨다 ->
Provider는 Token에 있는 계정정보가 유효한지 DB로부터 조회한다 ->
정보가 유효하면 Provider는 Token 을 발급시킨다. ->
발급된 Token은 Security Context에 저장된다. ->
계정 정보가 유효하면 Filter는 SusccesHandler에 따라 요청을 redirect 시킨다.
SpringSecurity의 Authenticate 과정을 그림으로 표현하면 이런 프로세스로 진행된다.
SpringSecurity Authenticate 진행과정
Spring Security 구현하기
- Maven dependency에 스프링 시큐리티를 추가한다.
- WeboSecurityConfig 클래스를 생성한다.
- WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter를 상속받는다.
- 다음과 같은 설정들을 추가한다.
- 어떤 요청에 대해서 인증을 요구할 것인지
- 특정 요청에 대해서 어떤 권한을 요구할 것인지
- 인증되지 않은 요청을 어떤 url로 redirect시킬지
- 로그인 성공 후 어느 화면으로 이동시킬지
- 로그아웃시 어떤 작업을 수행시킬지
- 403에러에 대해 어떻게 처리할지
- Authentication 유효성을 어떻게 판단할지
- configure 를 Override 해서 구현한다.
- AuthenticationSuccessHandler class 를 생성한다.
- SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler 를 상속받는다.
- 인증 성공 후에 Redirect시킬 URL을 설정한다.
- AuthenticationProvider를 구현한다.
- Authentication 을 Override 한다.
- 인증을 처리한다.
- AccessDeniedHandler 를 구현한다.
- 인증에 성공했으나, 권한이 적합하지 않을경우 403 에러를 발생시킨다.
SecurityConfiguraiton 예제)
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private AuthProvider authProvider;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.csrf().disable()
//csrf(Cross site request forgery) : 사이트 간의 요청 위조, Spring Security에서는 @EnableWebSecurity 어노테이션을 지정할경우 자동으로 CSRF 보호기능이 활성화 된다. 따라서 CSRF 비활성화가 필요할경우 csrf().disable() 설정을 추가해야한다.
.authorizeRequests()
// authorizeRequest() 요청에 대한 인증/권한 설정을 담당한다.
.antMatchers("/","main").permitAll()
// ("/", "main") 요청은 인증 체크를 하지 않는다.
.antMatchers("/admin/*").hasAnyAuthority("ADMIN")
// ("admin/*")에 해당하는 요청은 "ADMIN" 권한이 있어야 접근 가능하다.
.anyRequest().authenticated()
// 위에서 정의한 요청을 제외한 모든 요청에 대해서는 인증을 요구한다.
.and()
.formLogin()
// 로그인 관련 설정을 담당한다.
.loginPage("/login")
// 아직 인증 전 상태이며 인증을 요구하는 요청이라면 "/login" 으로 redirect 시킨다.
// 커스텀 로그인 페이지를 사용할때 사용
// 만약 해당 url 페이지가 없으면 404 not found 에러가 발생한다.
// 만약 프론트 로그인 페이지가 localhost:4200/Login 이면 그대로 적으면 된다.
// 이걸 사용안하면, Spring Security 에서 제공하는 로그인 폼을 자동으로 사용하게 된다.
.usernameParameter("userId")
// Spring Security에서 설정한 dafault 변수명인 username 을 userID 이름으로 변경시킨다.
.successHandler(new LoginSuccesHandler("/home"))
// 인증을 성공했을때 어떤 URL로 Redirect 시킬지 정의한다. 이를 위해 AuthenticationSuccessHandler 클래스를 생성해야 된다.
.permitAll()
.and()
.logout()
// 로그아웃 관련 설정을 담당한다.
.invalidateHttpSession(true)
// 로그아웃 요청이 오면 Session을 무효화 한다.
.deleteCookies("JESSIONID")
// 로그아웃 요청이오면 키-JESSIONID로 저장된 쿠키를 제거한다.
.permitAll()
.and()
.authenticationProvider(authProvider)
// 로그인 폼으로부터 오는 데이터가 유효한 계정 정보인지를 판단하기 위해 AuthenticationProvider를 구현했다.
.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedHandler(accessDeniedHandler());
// 인증에는 성공했으나 권한이 맞지 않을 경우 실행될 Handler를 등록한다.
}
- httpBasic() 메소드 : HTTP 기본 인증을 구성한다.
- 즉, HTTP STATUS 401, 403, 407 등 사용
AuthProvider 예제)
@Service
public class AuthProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
// AuthenticationProvider : 클라이언트로 부터 받은 AuthenticaionToken을 처리한다. (DB 조회해서 받은 인증과 일치하는지 등)
// 올바른 인증이면 새로운 authenticationToken 을 생성한다.
@Autowired
StudyAuthService studyAuthService;
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
String id = (String) authentication.getPrincipal();
// authentication.getPrincipal() : 인증되는 주체의 ID를 가져온다.
// 로그인 ID는 AuthenticaionToken의 principal 에 저장되어 있다.
String password = (String) authentication.getCredentials();
// getCredentials() : 인증이 올바르다는 것을 증명하는 자격증명을 가져온다. 보통 암호를 말한다.
// password 는 AuthenticaionToken의 credential에 저장되어있다.
StudyUser studyUser = studyAuthService.selectByID(id);
//DB에서 인증되는 주체에서 갖고온 ID를 검색한다. DB에서 해당되는 유저가 있으면 모든 정보를 가져온다. (Password까지 포함해서)
if(studyUser == null){
//DB에 해당되는 유저가 없으면 Exception
throw new UsernameNotFoundException(id);
}
if(!matchPassword(password, studyUser.getPw())){
//Authentication의 password 와, DB에서 가져온 password가 일치하지 않으면 Exception
throw new BadCredentialsException(id);
}
if(!studyUser.isEnabled()){
throw new BadCredentialsException(id);
}
ArrayList<GrantedAuthority> auth = new ArrayList<GrantedAuthority>();
// 권한 목록 리스트를 생성한다.
for(String authority : studyUser.getAuthority()) {
// 해당 유저의 권한 목록 리스트를 가져온다.
auth.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(authority));
//DB에서 조회한 해당유저의 권한 목록을 생성한 권한 목록 리스트에 넣는다.
}
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(studyUser, password, auth);
/**
* 새로운 AuthenticationToken을 생성한다.
* 파라미터로 받은 AuthenticationToken 과의 차이점은
* 1.) principal의 정보가 확장되었다. (loginId => DB로부터 조회한 User정보)
* 2.) 권한 목록을 3번째 파라미터에 추가한다. 이는 권한 체크를 할때 사용된다.
*/
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return false;
}
private boolean matchPassword(String loginPassword, String from_DBpassword) {
// DB에서 가져온 password와, Authentication 에서 가져온 password가 일치하는지 판단한다.
return loginPassword.equals(from_DBpassword);
}
}
LoginSuccessHandler 예제)
public class LoginSuccessHandler extends SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler {
public LoginSuccessHandler(String defaultTagetURL) {
setDefaultTargetUrl(defaultTagetURL);
}
}
RestAPI 로 SpringSecurity 구현하기
참고 사이트 :
https://cusonar.tistory.com/17
SpringSecurity Config 설정
- REST API 로 사용할 것이기 때문에 formLogin() 옵션은 사용하지 않는다.
- 회원가입 url, 중복 확인 url 은 접근을 허용한다.
- 그외에 /user 혹은 /admin 은 각각에 대한 권한을 요구한다.
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.NEVER)
// 사용자의 쿠키에 세션을 저장하지 않겠다는 옵션이다.
// NEVER : Security 등 내부적으로 세션을 만드는 것을 허용한다.
// STATELESS : 사용자의 쿠키에 세션을 포함한 아무것도 저장하지 않는다.
// Rest 아키텍쳐는 Sateless를 조건으로 하기때문에 되도록이면 stateless가 좋다.
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.OPTIONS, "/**").permitAll()
// 크롬과 같은 브라우저 에서는 실제 GET, POST 를 요청하기 전에 OPTIONS를 preflight 요청을 한다.
// 이는 실제로 서버가 살아있는지를 확인하는 요청이다.
// Spring 에서는 OPTIONS에 대한 요청을 자동으로 막고있다.
// 따라서 OPTIONS 요청이 들어와도 허용하도록 변경한다.
@Bean
public HttpSessionStrategy httpSessionStrategy() {
return new HeaderHttpSessionStrategy();
}
// HttpSession 전략으로 쿠키의 세션을 사용하는 대신 header에 'x-auth-token' 값을 사용할 수 있게 해준다.
.csrf().disable()
.sessionManagement()
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.OPTIONS, "/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/user/login").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/user/insertUser").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/user/existsId").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/user/existsName").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/user").hasAuthority("USER")
.antMatchers("/admin").hasAuthority("ADMIN")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.and()
.logout()
authenticationManagerBean() 을 오버라이딩 한다.
- 사용되는 인증 객체를 Bean으로 등록할 때 사용한다.
- @bean 어노테이션을 붙여서 다른 클래스에서도 authenticationManager 객체를 사용할수 있게한다.
- 다른 클래스에서 사용시에 @Autowired 어노테이션을 붙이면 일일히 new 객체를 안만들어도 된다.
@Override public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception { return super.authenticationManagerBean(); }
URL( /user ) 으로 시작되는 url 들을 컨트롤할 UserController 커스텀 클래스를 새로 만든다.
- AuthenticationManager 객체를 사용해야 되기 때문에 선언한다.
- @Autowired 로 Bean 객체를 주입해 따로 new 객체로 객체를 생성안해도 된다.
- SpringSecurity Config 에서 아까 @bean 으로 어노테이션 붙였기 때문에 다른곳에서도 가져다가 쓸수있음. (new 객체를 안해도됨)
로그인하면 사용자 정보를 저장할 AuthenticationToken VO 클래스를 새로 만든다.
- 별거없다. 걍 커스텀 클래스인데, 사용자 이름, 권한, 토큰 문자열 필드를 갖는 커스텀 클래스다.
- 필드 목록
- String username
- Collection authorities
- String token
- 필드들은 다 private로 선언해줘야 한다.
- get/set/constructer 를 만든다.
- @Data 를 붙여서 롬북으로 하면 안만들어도 될듯하다.
- 각 필드를 갖는 Construct 만 만든다. (생성자)
로그인 정보를 담는 Login Vo 모델 클래스를 만든다.
- 예제에서는 임의로 AhtenticationRequest 명으로 만들었다.
- 필드 목록
- String id;
- String password;
- 각 필드들은 private 로 선언해줘야 한다.
- 생성자는 안만들어줘도 된다.
- @Data 로 롬북 처리를 하면 될것같다.
다음과 같이 Login 을 처리할 API를 생성한다.
- 반환 자료형은 AuthenticationToken Vo를 반환하도록 API 컨트롤러를 만든다.
- 클라이언트로부터 받는 것은 JSON 객체를 받도록 한다.
- 객체 자료형은 AuthenticationRequest 를 받도록 한다.
- HttpSession 객체도 받도록 매개변수를 설정한다.
- API에서 총 받아야되는 매개변수
- RequestBody AuthenticationRequest 객체
- HttpSession 객체
로그인 API 전체 코드
@PostMapping("/login")
public StudyAthenticationToken Login(@RequestBody StudyAuthenticationRequest studyAuthenticationRequest, HttpSession httpSession){
String id = studyAuthenticationRequest.getId();
String password = studyAuthenticationRequest.getPassword();
// JSON 으로 받은 id 와 password 를 꺼내서 문자열 변수에 집어넣는다.
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken token = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(id, password);
// 요청받은 id 와 password 로 토큰 객체를 만든다.
Authentication authentication = authenticationManager.authenticate(token);
// 토큰 객체로 Spring Security 에서 설정한 인증 절차를 진행한다. 이때 SpringSecurity 에서 설정한 인증절차가 적용되어 진행된다.
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
// 인증 받은 결과를 SecurityContextHolder.getContext() 로 얻어온다.
// Spring Security context 에 해당 인증 결과를 설정한다.
// 이로써 서버의 SecurityContext 에는 인증값 설정이 완료된다.
httpSession.setAttribute(
HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository.SPRING_SECURITY_CONTEXT_KEY,
SecurityContextHolder.getContext());
// API 의 매개변수로 HttpSession 객체를 지정하면 session 을 받아올수 있다.
// session 값에 인증이 완료된 SpringSecurityContext 를 설정한다.
// 이때 속성키는 HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository.SPRING_SECURITY_CONTEXT_KEY 으로 넣어주면 된다.
StudyUser studyUser = studyAuthService.selectByID(id);
// 인증이 완료되었으면 해당 유저가 DB에 있다는 뜻이니 해당 유저의 정보를 가져와서 해당 유저vo 를 만든다.
return new StudyAthenticationToken(studyUser.getId(), studyUser.getAuthorities(), httpSession.getId());
// 해당 유저의 id , 권한, session ID 를 Toekn 객체로 만들어서 리턴한다.
}
AuthenticationManager
- 인증 절차 메소드를 모아둔 객체
- 등록한 AuthenticationProvvider들을 연쇄적으로 실행시킨다.
- AuthenticationProvider 들의 구현체에서는 다음과 같은 작업이 필요하다.
- 1) 매개변수로 들어온 Authentication 객체에 있는 계정 정보가 DB에 들어있는지 확인하는 작업
- 2) DB 에 계정 정보가 들어있으면 유저의 상세 정보를 이용해 새로운 UserPasswordAuthenticationToken 을 발급하는 코드 작성
- authenticate ( 인증받을 객체 ) 메소드를 실행하면 인증절차를 진행한다.
- 인증이 실패하면 BadCredentialsException 이 발생한다.
- 계정이 비활성화 된 경우 DisabledException 이 발생한다.
- 계정이 잠겨있는 경우 LockedException 이 발생한다.
- 계정의 ID 를 찾을수 없으면 UsernameNotFoundException 이 발생한다.
Spring Security Config 에 authenticationManagerBean() 을 오버라이딩 하면 원하는 시점에 AuthenticationManager를 사용할 수 있다.
- @bean 어노테이션도 추가로 달아야 다른곳에서 객체를 가져다가 쓸수 있다.
AuthenticationProvider
- AuthenticationManager.authenticate(인증객체) 를 실행할때 순차적으로 실행되는 인증 절차
- SpringSecurity Config 에 다음과 같이 커스텀 AuthenticationProvider를 등록할 수있다.
@Autowired
private AuthProvider authProvider;
// 사용자가 직접만든 커스텀 클래스
// 해당 클래스는 AuthenticationProvider를 implements 해야된다.
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
...
...
.authenticationProvider(authProvider);
Authenticate() 각 exception 별로 관리하는 방법
@RequiredArgsConstructor // add lombok inject
public class SecurityController {
private final AuthenticationManager authenticationManager; // @Autowired
// ...
@PostMapping(value = "/my-login")
public String customLoginProcess(
@RequestParam String username,
@RequestParam String password
) {
// 아이디와 패스워드로, Security 가 알아 볼 수 있는 token 객체로 변경한다.
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken token = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password);
try {
// AuthenticationManager 에 token 을 넘기면 UserDetailsService 가 받아 처리하도록 한다.
Authentication authentication = authenticationManager.authenticate(token);
// 실제 SecurityContext 에 authentication 정보를 등록한다.
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
} catch (DisabledException | LockedException | BadCredentialsException e) {
String status;
if (e.getClass().equals(BadCredentialsException.class)) {
status = "invalid-password";
} else if (e.getClass().equals(DisabledException.class)) {
status = "locked";
} else if (e.getClass().equals(LockedException.class)) {
status = "disable";
} else {
status = "unknown";
}
return "redirect:/login?flag=" + status;
}
return "redirect:/";
}
}
